Law of thirds
The internal intersection of lines (red dots) is where the main object should be located. |
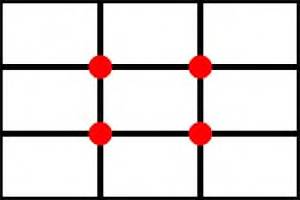
|
Horizon
The horizon line should be on the top internal line of the grid if the sky lacks clouds and may be on the bottom internal line of the grid if the sky has interesting clouds.
Foreground (the first 10 feet, midrange (10 to 40 feet), background (greater than 40 feet)
when shooting a general landscape. To get everything in focus use a small aperature (f16 to f64). To just get part in focus such as foreground then open up the aperature to (f2) or less. Using a telephoto lens may also help in just getting part of the picture in focus.
Soft focus
This is where the main subject is slightly out of focus. It is often used in head shots of older people.
Active vs. stable
Active pictures lead the eye around the photo using a sinuous line like a winding stream, spiral staircase, tree branches, etc. Diagonal lines make a photo active, whereas having only vertical and/or horizontal lines will make the photo stable. Usually a bright object or white will initially grab the person's eye and then they will look at the rest of the photo. Stable pictures have a target effect. The main subject is centered like the door of a house.
KIS
keep it simple. Don't try to get a lot of things in a photo. You want the main subject to stand out and not be lost in a lot of clutter.
Space
put more space in front of cars, people, animals than behind them. Pan with moving objects so they don't become blurred . Using a telephoto lens at it's maximium effect will help cut down blur particularly if the object is moving toward or away from you. The angle of the shot is important. A quick shutter speed (1/1000 second) helps alot to reduce blur.Some people will prefocus where the object will be and shoot when the object enters that space. This works well with racecars and horse races.
Contrast
is when there is a large difference between the dark parts of a photo and the light parts. Low contrast happens when a photo is taken on a cloudy day and the colors are muted or if shooting in black and white then there is a lot of grey. Contrast can be modified after a picture is taken either in a darkroom or a computer.
Lighting
For a flat looking photo have the light source right behind you or use a pop-up flash. To bring out texture or detail then have the light coming from the side. Many photographers only shoot in the first two hours after sunrise and just before sunset to get texture. This also gives a warmer feeling to a photo.Translucent objects like leaves will really jump out if the light is behind them and shines through the leaf. Be careful here to have the end of your lense in the shade.
When shooting people put the ones with dark clothing in the front (groom) and the lighter ones in the back (bride) as flash effect falls off with distance. If a flash is not going to be used then shoot faces on a cloudy day or in a shaded area, otherwise the contrast will be too great. To illuminate the dark side of an object place a reflector (white, gold, etc) to bounce light back at the object.
Shoot for dark and print for highlights is a common rule so the detail in the dark areas will show up. Again; post-processing in a computer or darkroom can get the picture to look like what you saw.
Odd numbers
Odd numbers are generally more pleasing to the eye and some randomness helps. We are talking about 3, 5, 7. After that there are just too many objects to make much of a difference.
Framing
Framing in this sense means putting something around the edge of a photo. This might be the trunk of a tree on one side with it's branches covering part of the top. You might shoot out through a window and use the window and it's frame in the photo.
Rhythm
is when you have multiple and simular objects, such as fence posts going off into the distance.
Convergence
everything to a point for example leaf veins to a petiole or a spiral.Shoot horizontally and vertically.
Shoot from unusual angle or things
Move around and look behind you***step back for landscape***step forward for portrait so you get head and shoulders. Composition by Johannes Vloothuis